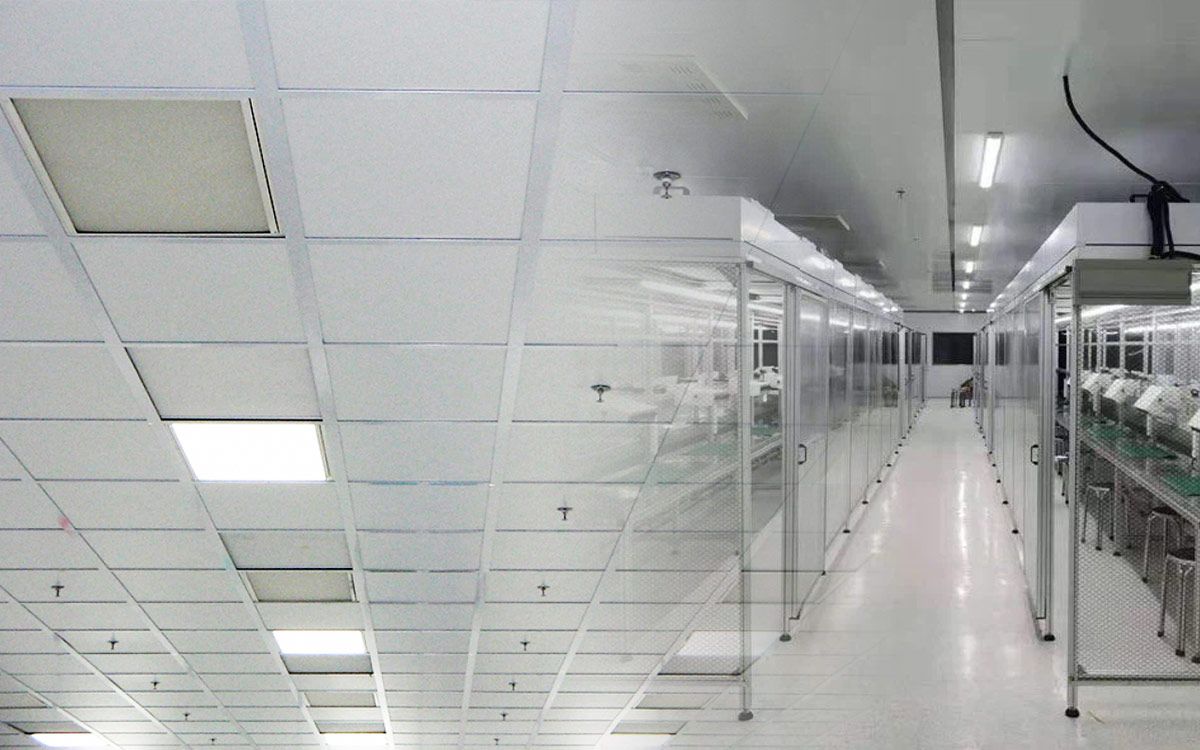
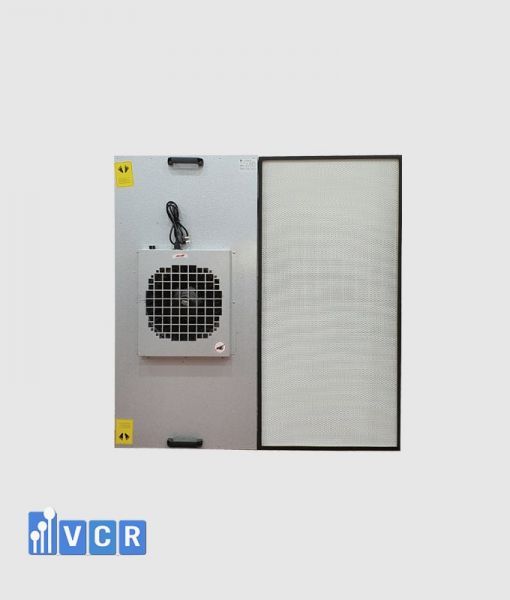
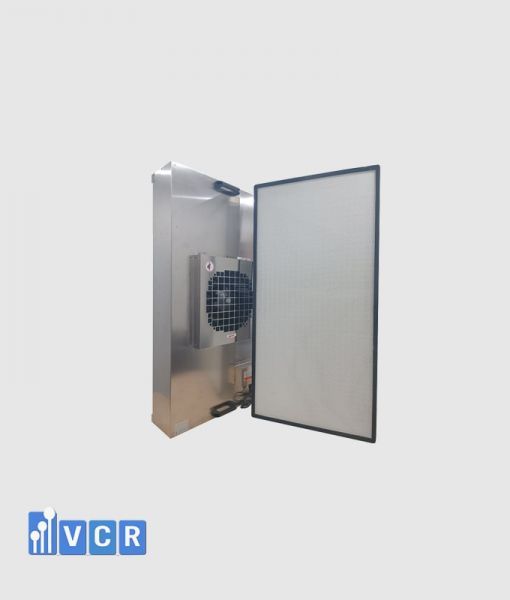
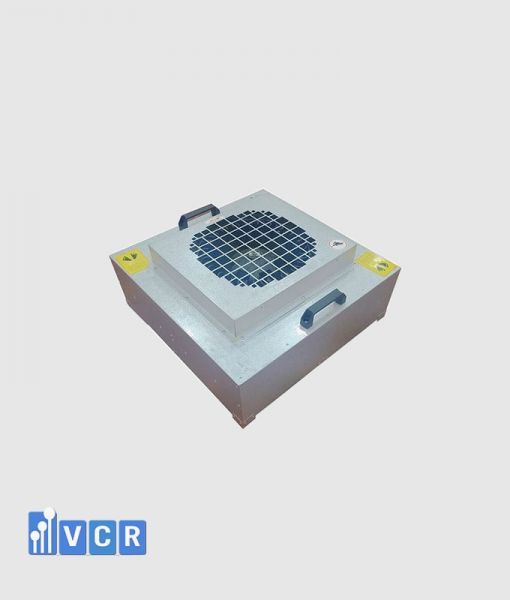
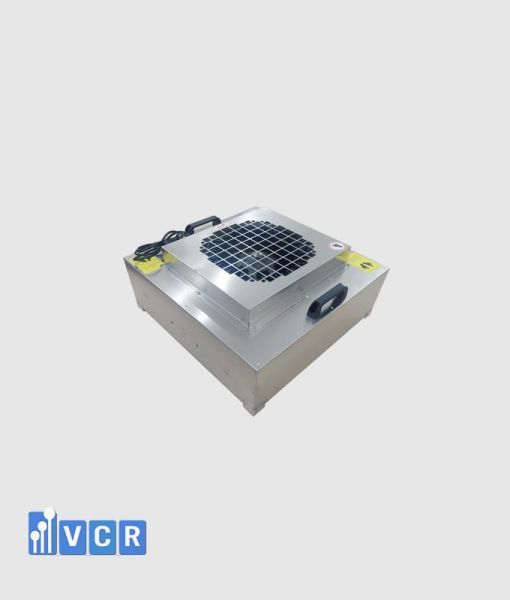
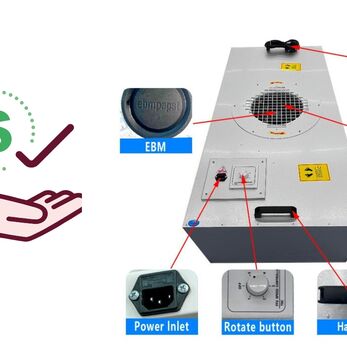
Fan filter units (FFUs) play a crucial role in maintaining pristine environments in cleanrooms by generating laminar airflow, a smooth, unidirectional air movement vital for controlling airborne particles.
Understanding the principles behind this airflow pattern and its maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal cleanroom performance.
The Power of Laminar Flow in Cleanroom
FFUs typically draw air through pre-filters and HEPA filters before releasing it at a constant speed, typically around 0.45 m/s with a 20% tolerance. This creates laminar flow, characterized by its straight, undisturbed path, effectively minimizing particle movement within the cleanroom.
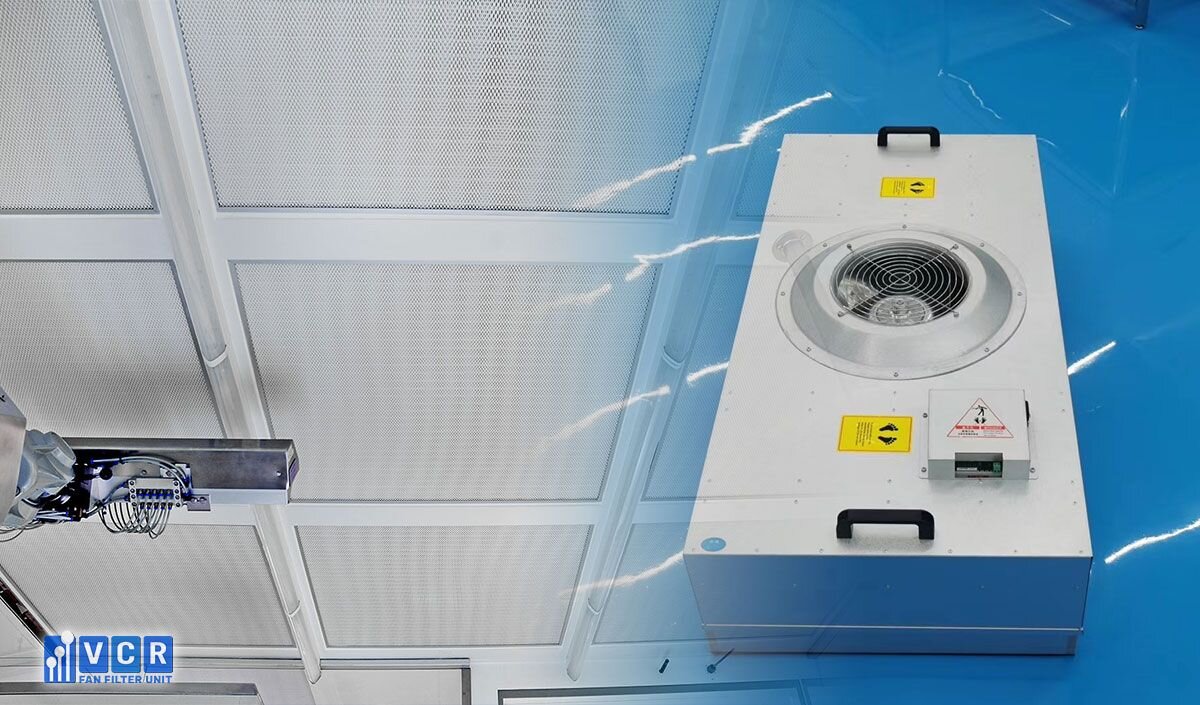

See more: When is a Fan Filter Unit Necessary for Clean Room
Balancing Velocity and Cost
Cleanroom airflow velocity plays a critical role in maintaining cleanliness. While the ideal range rests between 0.25 and 0.5 m/s, human activity can disrupt this delicate balance. Increasing air velocity to combat this disturbance may seem logical, but it comes at a cost - higher energy consumption. Striking the right balance between ensuring cleanliness and managing operational expenses is crucial.
See more: FFU Count for Cleanroom
FFU Maintenance: The Key to Consistent Cleanliness
Maintaining consistent laminar airflow requires meticulous FFU maintenance. If disruptions occur, the unidirectional flow weakens, jeopardizing the cleanroom's pristine environment.
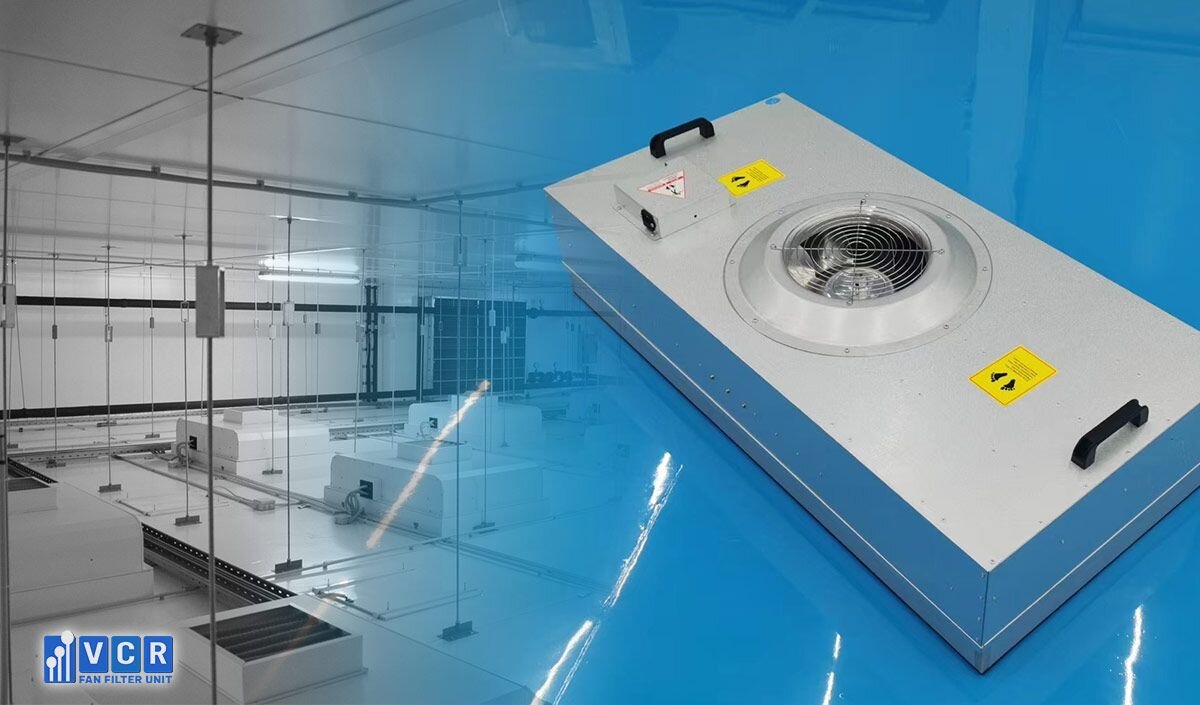

Here are key factors for maintaining optimal laminar airflow:
- Consistent Blowing Velocity: The air velocity emanating from the FFU's blowing surface must remain constant.
- Controlled Suction: The wind speed at the suction surface of the floor return plate needs to be stable.
- Avoiding Turbulence: Deviations from the recommended range (0.2-0.7 m/s) can lead to eddy currents, disrupting the laminar flow.
- Optimal Speed: A velocity of 0.5 m/s generally promotes uniform airflow distribution.
By understanding these crucial aspects of laminar airflow control in FFUs, cleanroom professionals can make informed decisions regarding maintenance strategies and operational parameters, ensuring a consistently clean and controlled environment.